|
|
|
| The rainbow - sun rays are refracted when entering and leaving a rain drop. Simultaneously a total reflection occurs at the backside of the drop. That's why the sun always stands behind the observer and the rainbow appears as a circle around the straight line from the sun to the observer to the midpoint of the rainbow circle (a rainbow cone of 42° opens in front of the observer). Because of the reflected light the inner area of a rainbow appears brighter than the area outside of the rainbow (Caustics). Additional reflections inside the rain drops may produce additional rainbows around the main bow but with rapidly fading intensities.
|
|
|
| In CyberMotion this physical model is adopted for the most part. If you switch on the rainbow effect, then not only simply color circles are drawn in the background. Instead the visibility of the rainbow depends on the position and point of view of the camera and the position of the sun. Therefore, if you want a rainbow to appear in the picture the sun has to shine from behind the camera. The best thing to do would be to set the camera zoom to a low value in order to locate the rainbow in the sky. Then, adjust the rainbow position by correcting the angle of light incidence for the sun and finally zoom in again with the camera.
|
|
|

|
| If you are lucky you can observe the real circular nature of a rainbow when looking out of a flying aeroplane. Back on the ground the lower part of the rainbow will be hidden again by the earth.
|
|
|

|
| Example rendering with a bright main rainbow and a dim secondary rainbow. The caustics effect was switched on to lighten the inner are of the rainbow. Furthermore the height was limited, so that the rainbow is fading with increasing height. If a complete arc can be seen depends among other things on the height and expansion of the rain clouds.
|
|
|
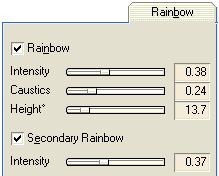
| The parameters:
|
| Intensity - controls the intensity of the main- and secondary rainbow colors. Since the intensity of the secondary rainbow is always falling off against the intensity of the main rainbow, it is only calculated as a fraction of the intensity of the main rainbow.
|
| Caustics - defines the brightness of the caustic reflections within the rainbow.
|
| Height° - limits the height of the rainbow in dependence on the maximum opening angle of the rainbow (main bow 42°, secondary bow 51°)
|


